Google AI Lab’s researchers are developing a robot that can replicate the agile behavior of a real dog. The team of researchers are now seeing results in their effort to develop a quadruped dog-like robot which learns a real dog’s behavior by studying their movement through video clips.
Machine learning techniques have been around since the earliest times of artificial intelligence (AI) development and their usage in robotic systems is increasing at a rapid pace. For example, Google Maps use AI and machine learning techniques to determine the fastest route available, Tesla’s self-driving cars use these techniques to drive without a driver and so on. However, Google is now teaching it’s dog-like robot by showing it recorded video clips of a real dog which is definitely a new technique.
Google’s dog-like quadruped robot is called Laikago (named after Laika, the first dog in space) – it is being trained to hop and turn, run fast, walk and even chase its tail like a real dog by showing it the reference motion clip recorded from an animal (a dog, in this case).
The first step in motion imitation is to collect the motion capture clips of a real dog performing these locomotion skills. Then Reinforcement Learning (RL) technique is used to train a control policy (simulation) to imitate the dog’s motion. The policies are then trained in a physics simulation to track the pose of the reference motion at each timestamp. Then, by using different reference motions in the reward function, they can train a simulated robot that imitate a variety of different skills.
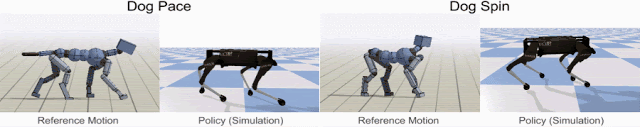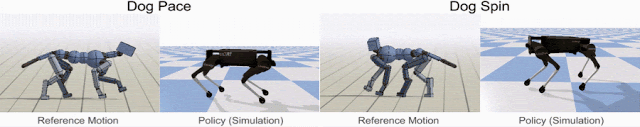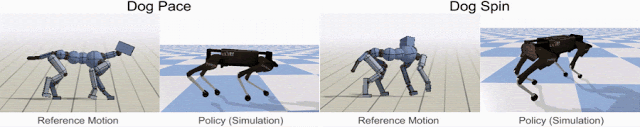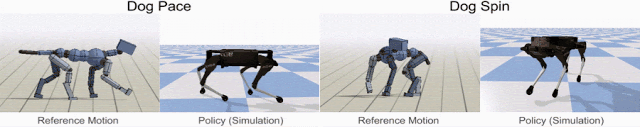
The following video of Laikago shows how the techniques work in action.
Laikago, as compared to more advanced robots such as those from Boston Dynamics, which get their skills via programming is still a little weak but Google’s AI researchers and engineers are undaunted, believing more research will even lead to ever more lifelike behavior by their robots.
The researchers at Google AI Lab are interested in applying the automated training system to more complex real-world environments and tasks. The researchers have published a summary of their work on Google AI Blog.




![Types of Engineers and What they Do [Explained]](https://www.engineeringpassion.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/types-of-engineers-and-what-they-do-280x210.jpg)








Leave a Reply